
The report also shed light on a growing problem in which consumer data (including credentials) is being compromised in data breaches, which can then be used to propagate further attacks. However, the study also found that those who were further along in their overall cloud modernization strategy (“mature” stage) were able to detect and respond to incidents more effectively – 77 days faster on average than those who were in early-stage adoption.Īdditionally, for cloud-based data breaches studied, companies that had implemented a hybrid cloud approach had lower data breach costs ($3.61m) than those who had a primarily public cloud ($4.80m) or primarily private cloud approach ($4.55m). Nearly 20% of organizations studied reported that remote work was a factor in the data breach, and these breaches ended up costing companies $4.96 million (nearly 15% more than the average breach).Ĭompanies in the study that experienced a breach during a cloud migration project had 18.8% higher cost than average. The report found that these factors had a significant impact on data breach response. With society leaning more heavily on digital interactions during the pandemic, companies embraced remote work and cloud as they shifted to accommodate this increasingly online world. “While data breach costs reached a record high over the past year, the report also showed positive signs about the impact of modern security tactics, such as AI, automation and the adoption of a zero trust approach – which may pay off in reducing the cost of these incidents further down the line.” Impact of remote work and shift to cloud on data breaches “Higher data breach costs are yet another added expense for businesses in the wake of rapid technology shifts during the pandemic,” said Chris McCurdy, VP and General Manager, IBM Security. For cloud-based data breaches studied, organizations that had implemented a hybrid cloud approach had lower data breach costs ($3.61m) than those who had a primarily public cloud ($4.80m) or primarily private cloud approach ($4.55m). The adoption of AI, security analytics, and encryption were the top three mitigating factors shown to reduce the cost of a breach, saving companies between $1.25 million and $1.49 million compared to those who did not have significant usage of these tools. The combination of these factors could cause a spiral effect, with breaches of username/passwords providing attackers with leverage for additional future data breaches.
At the same time, customer personal data (such as name, email, password) was the most common type of information exposed in data breaches – with 44% of breaches including this type of data. Stolen user credentials were the most common root cause of breaches in the study. Compromised credentials led to compromised data Healthcare breaches cost the most by far, at $9.23 million per incident – a $2 million increase over the previous year. Industries that faced huge operational changes during the pandemic (healthcare, retail, hospitality, and consumer manufacturing/distribution) also experienced a substantial increase in data breach costs year over year.

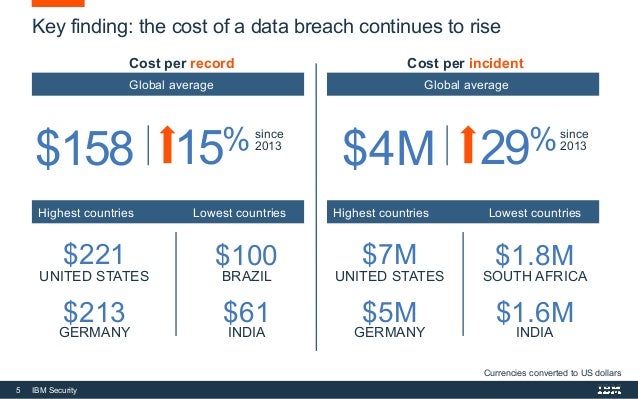
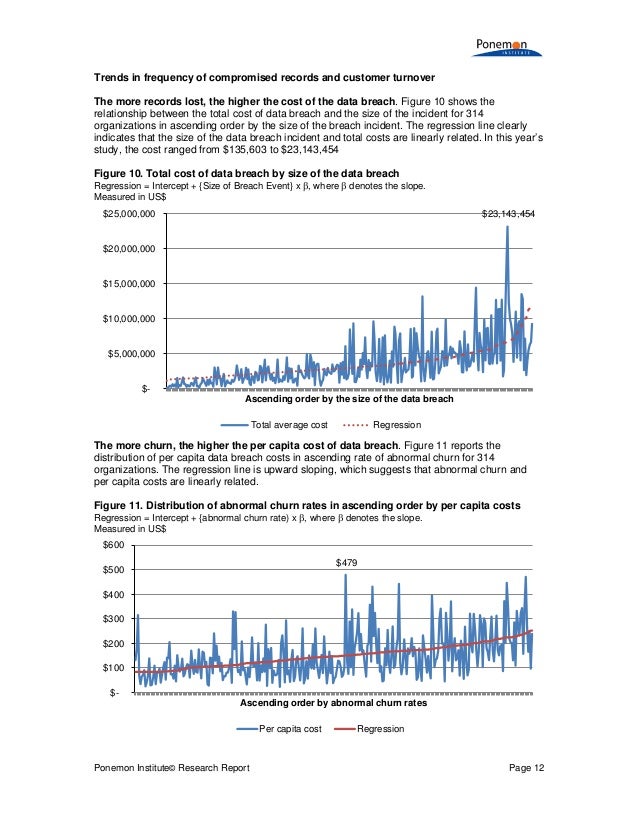
$3.89 million.) Healthcare breach costs surged Breaches cost over $1 million more on average when remote work was indicated as a factor in the event, compared to those in this group without this factor ($4.96 vs. The rapid shift to remote operations during the pandemic appears to have led to more expensive data breaches. The new findings suggest that security may have lagged behind these rapid IT changes, hindering organizations’ ability to respond to data breaches. Data breaches now cost companies a total of $4.24 million per incident on average, according to the Cost of a Data Breach Report, conducted by Ponemon Institute and analyzed by IBM Security.īased on in-depth analysis of real-world data breaches experienced by over 500 organizations, the global study suggests that security incidents became more costly and harder to contain due to drastic operational shifts during the pandemic, with costs rising 10% compared to the prior year.īusinesses were forced to quickly adapt their technology approaches last year, with many companies encouraging or requiring employees to work from home, and 60% of organizations moving further into cloud-based activities during the pandemic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
